Overview
What is varicose vein?
This is a disease of human circulation system, occurring especially in veins and most commonly in legs. Varicose veins in legs are more prevalent in the area between the patella and the ankle. Impairment of the venous valves in this area leads to dysfunction.
Why do Varicose Veins occur?
Veins circulate the oxygen-poor venous blood upwards from legs to the heart. There are 5 to 7 valves in between the ankle and the knee to prevent leakage of the venous blood backwards due to the gravity. These valves open and close in a cyclic manner to prevent the reflux of venous blood. However, venous blood leaks backwards and accumulates in veins, where these valves do not function properly due to various reasons. This accumulation dilates the veins that bulge and cause bumps on the skin. Ultimately, varicose vein disease develops that is also called dilated veins.
Various health problems can be inherited from parents through genetic codes at birth; therefore, varicose veins in your mother and father pose a risk for you. The risk increases by 2-fold if the problem is present in your mother. Of course, genetics are not the only reason.
The pressure that builds up in blood vessel is a significant cause for dysfunction of venous valves. The pressure generally increases due to standing or staying still for long periods of time. For example, a hair dresser stands stationary while working during the day. If these individuals do not walk or lie down and elevate their legs 20-30 cm above chest level for 30 to 60 minutes, the pressure cannot be relieved and therefore, the valves are damaged. Hence, we should disperse the pressure in our vessels by walking, moving, lying down, even putting a pillow beneath our legs to keep them 20-30 cm above the chest level.
What Are Symptoms Of Varicose Vein? How Can It Be Recognized?
While it does not show any symptoms at initial stages, even the patients can recognize varicose vein when they emerge prominently. Dilation of vessels leads to bulging towards skin as the disease progresses. It is the most typical sign of the condition, but other disturbing symptoms may also develop.
Itching and pain occur in legs especially on evenings due to bulging of veins into the skin. Similarly, these patients suffer from cramps more frequently. It is necessary to lie down and keep your feet 20-30 cm above the chest level by putting a pillow beneath your legs to alleviate the pain. Pain in your leg will regress this way.
Dilated vessels not only bulge into the skin, they also cause skin cracks after a certain stage. This situation, which is called “varicose vein hemorrhage”, is a critical condition and compression might be necessary to stop bleeding in some cases. These hemorrhages lead to persistent scars in legs and varicose ulcers. Varicose Ulcer is the most challenging stage that causes necrosis in legs.
What are protective measures?
Learn if your mother and father have history of varicose vein and its treatment. You should take precautions if their answer is yes. The first action you must take is to avoid standing stationary for a prolonged period of time while working; if you have no other choice while working, leave your working area at 30- to 60-minute intervals to walk or lie down, if possible. Sometimes, protective measures may not help, as the disease can also be inherited.
How is Varicose Vein Treated?
The permanent solution for varicose veins is surgical intervention, but there are other options, such as Varicose Vein surgery and non-surgical modalities.
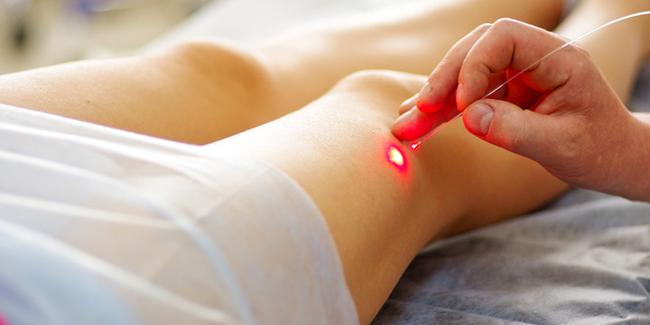
Non-surgical methods: there are 4 different methods which can be applied over skin and through endovascular route; laser and radiofrequency methods are applied on the skin, while foam and cclerotherapy are endovascular modalities that involves administration of a drug into the blood vessel using a thin syringe. Percutaneous (over the skin) treatments are preferred for capillaries that are not appropriate for puncture.
Varicose Vein Surgery: This is a very primitive treatment modality which is, unfortunately, performed in facilities with insufficient technological equipment or no cardiovascular surgeon. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and a hospital stay of 3 to 7 days is followed by resting at home for 20-45 days.








